What Are Terpenes in Cannabis and How Do They Work?
As the aromatic compounds found in all plants, including cannabis, terpenes are responsible for the flavor, aroma, and sometimes effect. Terpenes are truly the largest differentiators between cultivars (“strains”).
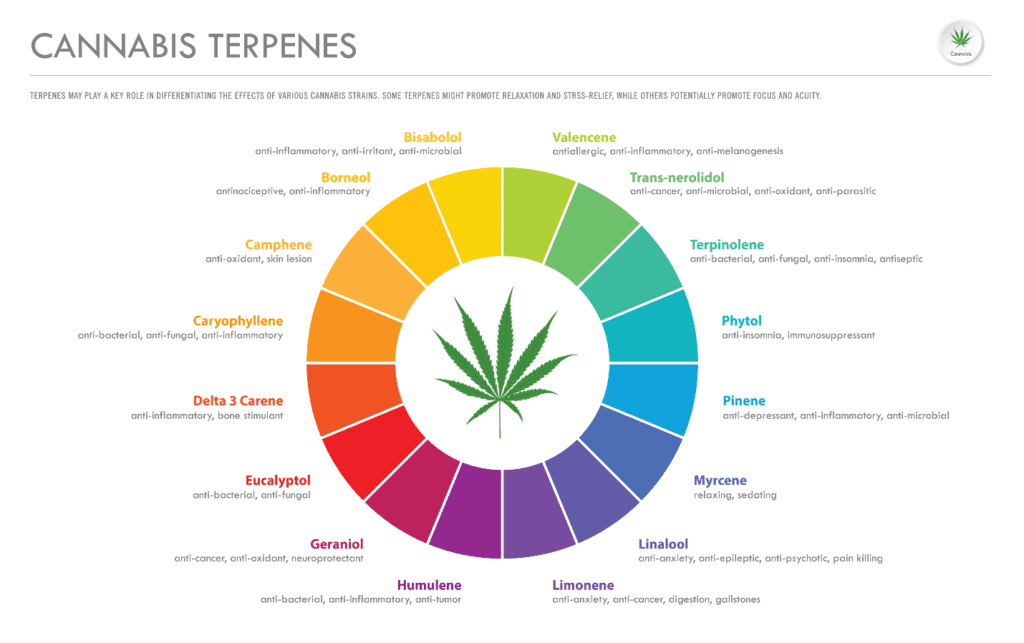
In detail, terpenes are a diverse group of organic compounds found in many plants, including cannabis. There are over 200 different terpenes that have been identified in cannabis, and each one has a unique aroma and flavor profile.
Scientists have recently begun discovering that terpenes not only affect the flavor and aroma of cannabis, but they might also influence the effect you get from the cannabinoids in your medicine. It was previously thought that cannabinoids were the only part of the plant responsible for the “psychoactive” effect.
Still, now scientists theorize that terpenes come into play with cannabinoids and can increase and intensify effects. Two strains with the same cannabinoids but with different terpenes may be able to produce many other effects as your body doesn’t ingest them in the same manner. Cannabis contains over 100 Terpenes, each with its own unique benefits.
How Do Terpenes In Cannabis Work?
If we want to explain terpenes and their effects, it would be best to discuss their interaction with the bodies. Terpene interaction with certain receptors can elicit biological responses affecting sleep, stress, mood, appetite, pain, inflammation, and more.
Terpene interaction with cannabinoids is often referred to as “the entourage effect,” in which a cast of compounds works together to maximize their therapeutic potential. Terpenes can moderate certain THC effects by limiting or increasing their absorption into the body and reducing its negative side effects.
Different Types Of Terpenes And Their Effects
There are hundreds of terpenes in the natural world, and the advancement of medical cannabis is leading to more research on the medical and therapeutic properties and benefits of these natural compounds.
A cannabis strain might contain several terpenes, affecting its smell and effectiveness. Below you will find an overview of the major kinds of these compounds to better help you understand their role in your medicine.
Some of the most common terpenes found in cannabis include:
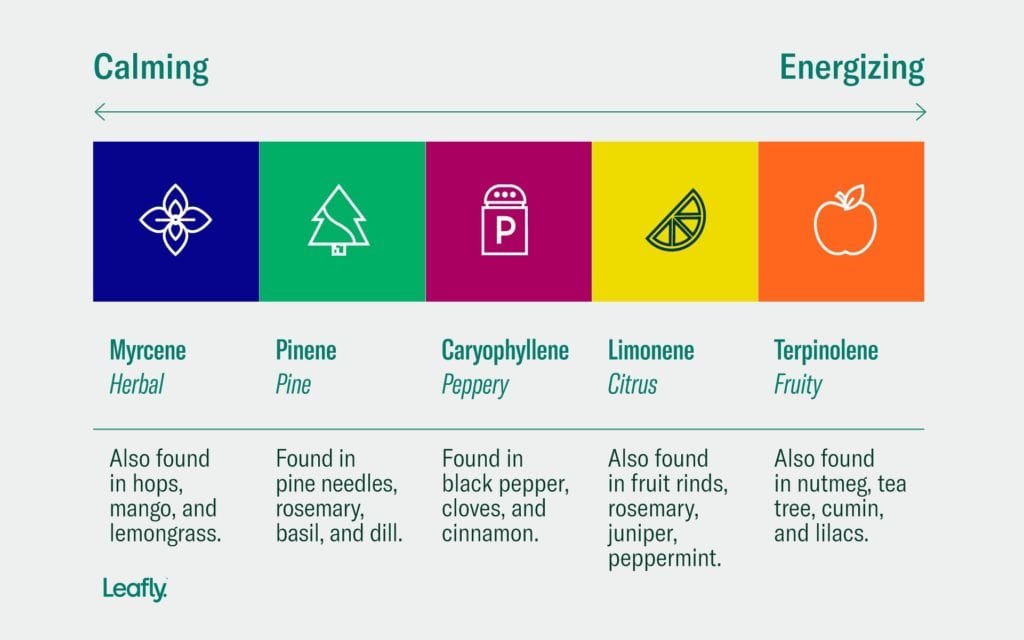
1. Alpha Pinene AKA Pinene
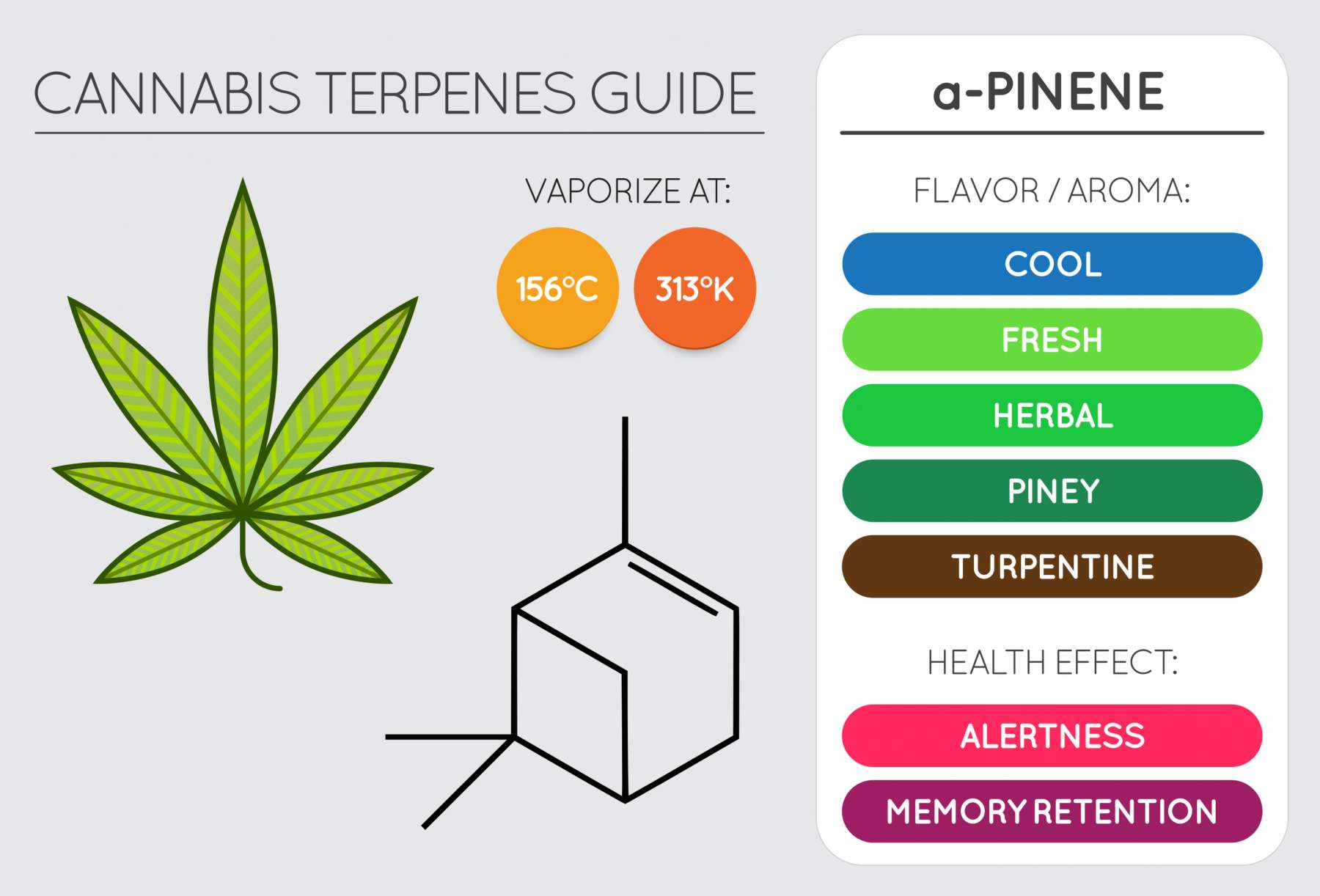
Alpha Pinene, better known as Pinene, has a woody aroma and is found in pine needles and other conifers. The terpene pinene comes in two isomers, alpha-pinene and beta-pinene, with alpha-pinene being more abundant in cannabis.
Its therapeutic effects include:
- Bronchodilator (allows more air into the lungs)
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antiviral
- Antimicrobial
Alpha Pinene has bronchodilator properties, with possible implications for treating asthma and other lung conditions. It is known to produce focus, improve memory and help with creativity, and may show promise as a supplement for those living with dementia-related diseases. Alpha Pinene also holds anti-bacterial properties towards certain bacteria, including Staphylococcus and Streptococcus.
Pinene is currently being researched for its anti-inflammatory properties and potential for pain management for those living with inflammatory conditions, including arthritis, cancer, and Crohn’s. It is also believed to have anti-cancer properties and improve mental clarity and alertness.
2. Caryophyllene or Beta-Caryophyllene
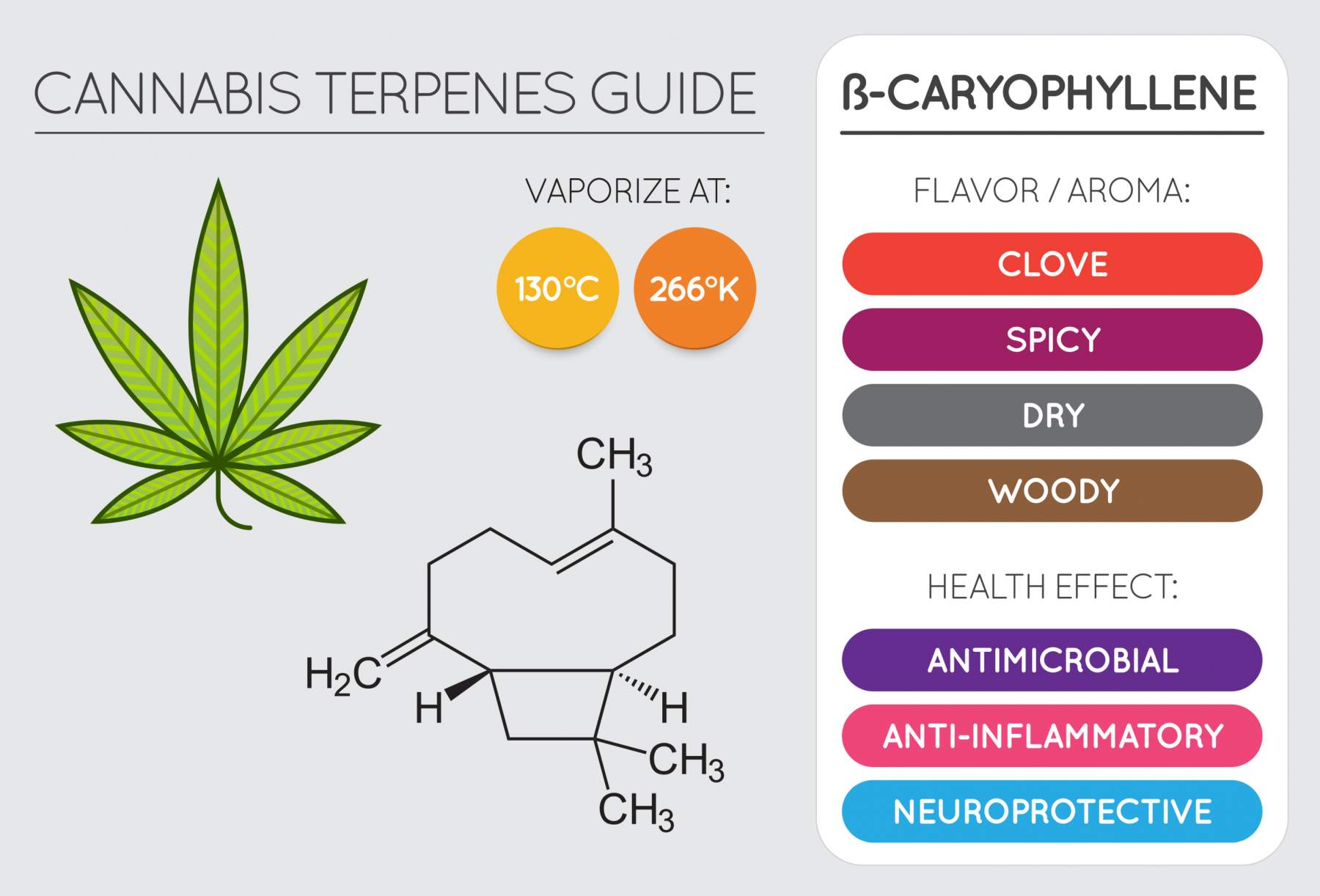
Beta-caryophyllene is mostly recognized for its spicy, peppery aroma, as it is also the dominant terpene in black pepper, and has a uniquely large size and structure. Also found in cloves and cinnamon, Caryophyllene is believed to have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties and may help reduce anxiety and depression. One animal study found that it reduced pain from inflammation and nerve pain. Other therapeutic benefits include:
- Anti-anxiety
- Antimicrobial
- Antibacterial
- Reduces cholesterol
Beta-caryophyllene can activate several receptors in the body, including the CB2 of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS), demonstrating analgesic properties that may act as an antioxidant for the liver, and it may also help control gastric acids. Beta-Caryophyllene has also shown analgesic properties with the potential to help people find relief from neuropathic pain.
It may also reduce inflammation in the brain by decreasing the chemicals that cause inflammation-induced stress. One animal study demonstrates Beta Caryophyllene’s potential to reduce alcohol intake.
3. Humulene
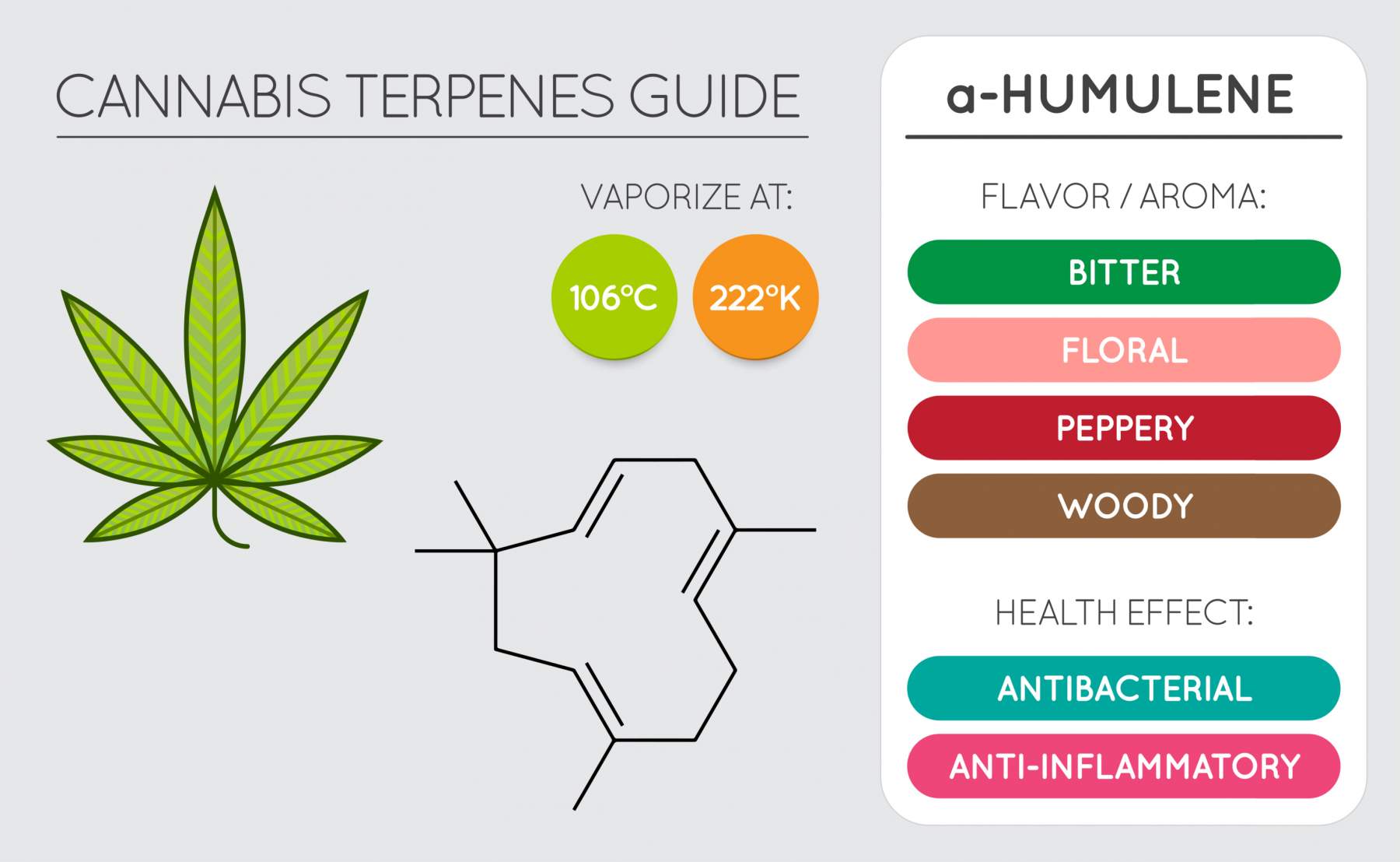
For anyone who appreciates beer, humulene may be a familiar terpene, as it is not only in cannabis, but it is the most abundant terpene in hops, which gives beer its flavor and aroma. Humulene is also found in common sage, black sage, balsam fir, ginseng, spearmint, and ginger.
Humulene is unique as it acts as both a terpene and a cannabinoid, meaning that it binds to the cannabinoid receptors much like THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids do. One study found that it may potentially prevent asthma and allergic reactions. Other therapeutic benefits of humulene include:
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anti-tumor
- Antibacterial
- Anti-pain
This terpene is considered a secondary terpene because it appears in lesser quantity than the more dominant terpenes.
When humulene found in black sage was researched, it showed to have possible anti-inflammatory attributes, suggesting that humulene may be helpful in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Humulene found in balsam fir was also discovered to hold anti-bacterial properties, particularly being effective against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
Humulene is also a powerful insect repellent. Humulene is being increasingly researched for its potential anti-cancer and anti-tumor properties, as it’s believed that humulene has a role in the depletion of natural oxygen within cancer cells.
4. Myrcene
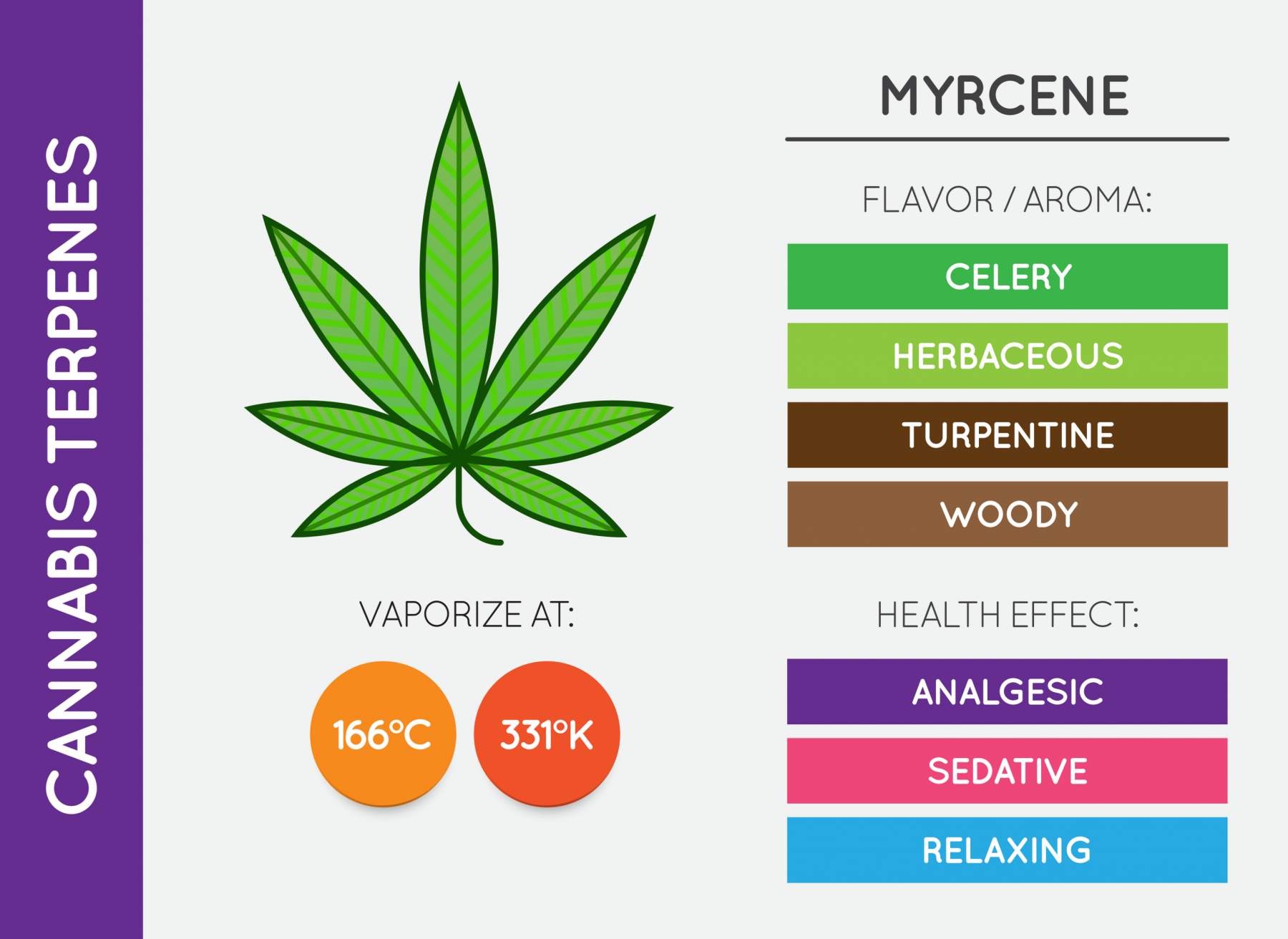
Myrcene: This is the most abundant terpene found in cannabis. Myrcene is found in hops, lemongrass, mango, and thyme, as well as the flowers of the cannabis plant. It has a musky, earthy aroma and is believed to have sedative and analgesic properties and may also enhance the effects of THC.
This terpene is a powerful antioxidant, with one study of mice finding that it can help protect the brain from oxidative damage after a stroke. In another mouse study, it was found that myrcene has a similar protective effect on the heart’s tissue. Other therapeutic effects of myrcene include:
- Anti-anxiety
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anticancer
- Anti-tumor
- Antioxidant
- Antidiabetic
Myrcene, as a monoterpene, isn’t one of the most well-known terpenes, but it is the one that’s found the most in cannabis plants, appearing in percentages of up to 65% in some strains. As for the effectiveness, it is the terpenes and THC relationship that is worth discussing. This terpene increases cannabinoid absorption, producing a much faster and more intense effect.
Myrcene is mostly known for its sedative effects, used in plant medicine over centuries worldwide as a tranquilizer and muscle relaxant. Initial animal studies have shown that when administered myrcene for its pain relieving properties, animal subjects experienced increased rest and time asleep.
While this theory is only preliminary, some scientists claim that myrcene can reduce pain by increasing the brain and spinal cord’s opioid chemicals. Myrcene also holds antioxidant attributes, protecting cells against toxicity, as well as potential anti-microbial properties.
5. Linalool
Having a lavender-like floral aroma, Linalool is found in lavender, mint, and coriander. Linalool is believed to have sedative and anxiolytic properties and may help reduce pain and inflammation.
This terpene is abundant in the lavender plant and gives it its rich scent.
Linalool’s therapeutic properties include the following:
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antimicrobial
- Neuroprotective
- Antidepressant
- Anticancer
- Anti-anxiety
Linalool is often related to relaxing and calming effects. Most detected in lavender, linalool is in over 200 plants and is one of the most popular alternative medicine sleep aids in the world.
As one of the best-smelling terpenes, Linalool is known mostly for its sedative effects, with animal studies confirming that it produces sedation without losing motor function. Other animal studies observe that Linalool can produce feelings of relaxation and counteract anxiety (when inhaled), produce anti-inflammatory effects to sources of inflammatory pain, or may have anticonvulsant properties.
Studies on addiction prevention see the potential of linalool via lavender therapies to reduce dependence on opioids post-operation. It may help restore lung health for smokers, with another study observing that it inhibits smoke-related lung inflammation.
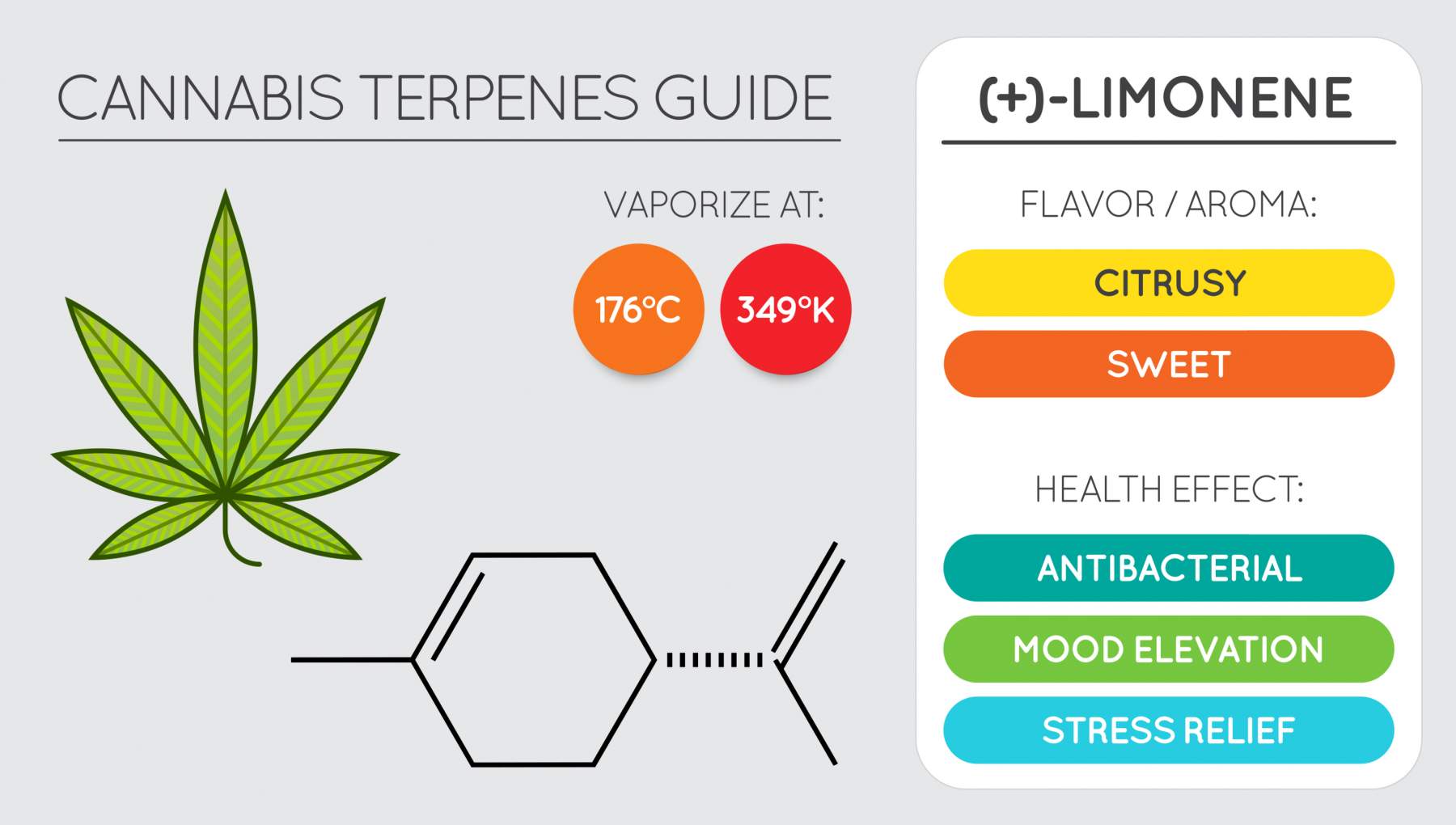
6. Limonene
Limonene is one of the most recognizable terpenes for its citrusy aroma and flavor. It is most commonly found in citrus fruits, especially limes, lemons, and oranges. When you cut into a lemon or lime, that zesty, fresh scent of the rind emits limonene.
This common terpene is quickly recognized by its smell, which is citrusy, as the name suggests. Limonene’s therapeutic properties include:
- Anti-inflammatory
- Antioxidant
- Antiviral
- Antidiabetic
- Anticancer
- Boosts focus
Limonene is one of the most popular terpenes due to its energetic, invigorating properties. Abundant in all citrus fruits, Limonene is highly valued for its anti-anxiety properties, with animal studies observing decreased anxiety and depression when limonene is administered.
Also known as an anti-oxidant, Limonene holds anti-inflammatory attributes that can affect how pain is signaled to the brain. Practitioners believe that this citrusy terpene can contribute to pain management.
Finally, limonene is being researched for its anti-cancer properties, with research supporting its potential ability to attack and kill cancer cells in studies of lung cancer, prostate cancer, and colon cancer.
In conclusion, terpenes are an essential component of cannabis, and they play a vital role in the aroma, flavor, and therapeutic properties of the plant. With further research, we may be able to unlock the full potential of these compounds and develop new cannabis-based medicines that can help to treat a wide range of medical conditions.
Did you learn something new? Let us know, or share the knowledge on social media! Unlock the benefits of terpenes by getting your medical cannabis card today.